Raster vs Vector
Raster vs Vector images, which is best and the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Raster Images
A raster image is an image that is made up of tiny square pixels, displayed in a matrix or grid. If you open a photograph on your computer or device and zoom in close, you’ll see the individual pixels.
Therefore, if a raster image is scaled up in size you will start to see the image become pixelated especially around the edges. Although a raster can be scaled down without any distortion.
Raster images are generally better for detailed complex images, such as a photo or a digital painting that contains lots of complex effects.
Large file sizes
With a raster image, if the pixels are increased then so does the file size. So, for example 3872 x 2592 pixels will be over 10 million pixels! (10mb)
The most common raster file formats are JPG, PNG, TIF. The software needed to edit raster images are photo or raster editing programmes such as Adobe Photoshop, Corel Paint Shop Pro and GIMP. GIMP is a free open-source program.
Vector Images
A vector image doesn’t contain any pixels, it’s created using mathematical equations and is composed of paths, basic shapes and anchor points.
A vector can be enlarged to any size and will always remain sharp. Think billboard size or graphics on the side of a truck! This is the main advantage of a vector graphic.
Small file sizes
The file sizes of vectors are usually quite small and remain the same size no matter what size the graphic has been resized to. Although in some cases the vector file size will increase if the artwork is enlarged. But this will be because raster effects may have been applied, such as a drop shadow or glow effects. So technically, the file is not 100% pure vector.
The most common vector file formats are AI, EPS, SVG and PDF. The most popular vector editing software used by far is Adobe Illustrator. But there are others such as CorelDRAW and Inkscape. Inkscape is a free open-source program.
Raster or Vector to create digital art
The answer to this question is that it depends on the type of artwork you like to produce. If you like to create art in the traditional style of painting, then working in raster would be the best option. It’s much easier to create realistic painting effects and textures using raster in Photoshop.
Working with raster in Photoshop, you would most likely paint with the brush tool as in the traditional painting method.
If you like to create clean illustrations, cartoons, logos and lettering work, then working in vector is the better option. It’s much easier to edit vector objects, such as changing the colours and altering and resizing shapes.
You can also paint or draw in Adobe Illustrator, but not to the same level as it would be if using Photoshop. It’s really more suited to drawing using the Pen Tool for more accurate results.
Combining Raster and Vector
It is possible to combine both vector and raster images. For example, you might find it easier to create the linework in Illustrator and then carry on working on it in Photoshop. You can paint with an endless variety of brushes or perhaps add complex textures for a more organic look.
Or if you create your artwork in Photoshop, you might want to open it in Illustrator to add some text if you are perhaps creating a flyer or poster for example.
Conclusion
So to summarize, there are pros and cons for working with raster or vector graphics and it really depends on the type of work or graphics you produce.
We’ve tried not to use too much technical jargon, so we hope it wasn’t too confusing and you found this article useful.
| RASTER | VECTOR |
|---|---|
| Raster images are composed of square pixels | Vector images are composed of lines, curves and anchor points |
| Rasters lose quality when upscaled | Vectors remain sharp at any size |
| Large high resolution images have large file sizes | Large vector images generally do not have large file sizes |
| Rasters are best for detailed images such as photographs or images that contain complex effects. | Vectors are better for less detailed images such as logos, illustrations, diagrams and text. |
| A raster is one object. | A vector can be made of many components and be easily edited |
| Typical file formats: JPG, PNG, BMP, GIF | Typical file formats: AI, EPS, SVG, PDF |
| Typical software used to edit raster images: Photoshop, PaintShop Pro, Affinity Photo |
Typical software used to edit raster images: Illustrator, CorelDraw, Inkscape |
Converting Raster to Vector
Usually, the best and most accurate way to convert a raster image to a vector graphic is to manually redraw it. If you’re new to working with vector this can be difficult, but there are lots of companies online that provide a vector conversion service at low cost.
You can also ‘Image Trace’ your artwork, but this rarely produces satisfactory results. This can also be done online or using software such as Adobe Illustrator.
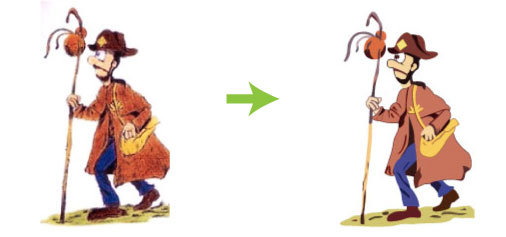
Converting Vector to Raster
Once you have your artwork in a vector format, it’s easy to convert it to a raster image. First you would need to establish the size of the raster image that’s needed. Then resize the vector to that size and then save the file as a raster file, such as JPG or PNG. You would need to select either 72dpi for web use or 300dpi for print.


